Introduction
Turbines play a critical role in the oil and gas industry, serving as key components in various processes including power generation, natural gas compression, and fluid pumping. These machines convert energy from various sources into mechanical energy and facilitate the extraction, transportation, and processing of hydrocarbons. Understanding the different types of turbines, their applications, design considerations, and components is essential to optimizing performance and reliability in the oil and gas sector.
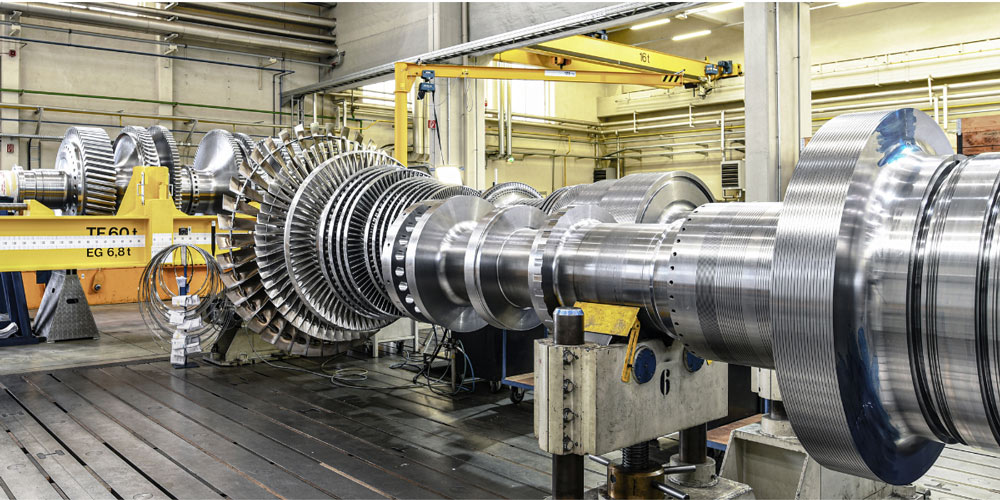
Application
Turbines are used in several applications in the oil and gas industry, including:
- Power generation: Gas turbines are commonly used in power plants to generate electricity needed for operations in remote locations.
- Gas compression: Turbines drive compressors that increase the pressure of natural gas for transmission through pipelines.
- Pumping systems: Turbines are used in pump drives to move fluids such as crude oil and refined products through pipelines.
- Mechanical Drive Applications: They are used to drive various equipment including separators, heaters and other process equipment.
- Offshore platforms: Turbines provide power to drilling rigs and production platforms located in offshore environments.
Types (Classification)
Turbines can be classified based on various criteria:
- By fluid:
Gas turbines: Use natural gas or other gases as the working fluid.
Steam turbines: Use steam generated from water heated by combustion or other heat sources.
Hydraulic turbines: Use flowing water to generate power.
Design
The design of turbines in the oil and gas industry is influenced by several factors:
- Efficiency: High efficiency is critical to reducing operating costs. Designers focus on optimizing aerodynamic profiles and minimizing losses.
- Material selection: Turbines must withstand harsh environments including high temperatures and corrosive materials. Materials such as Inconel, titanium alloys, and stainless steel are commonly used.
- Size and scale: The design must meet the specific requirements of the application, whether for large-scale power generation or smaller offshore installations.
- Cooling systems: Effective cooling methods are essential to maintain performance and longevity, especially in gas turbines.
- Control Systems: Advanced control systems are integrated to monitor and optimize performance under varying load conditions.
Spare parts
Maintaining operational efficiency requires a robust inventory of turbine spare parts:
- Blades: Replacement blades for both the compressor and turbine sections are critical to maintaining performance.
- Seals and gaskets: Essential to prevent leaks and ensure proper operation of various parts.
- Bearings: High-performance bearings are required to support rotating components under load.
- Fuel nozzles: Vital to ensure optimal mixing of fuel and air in the combustion chambers.
- Control systems components: Includes sensors, actuators, and electronic control units that monitor turbine performance.

